What Are the ASU Supercomputers?
ASU Research Computing provides high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructure and expertise to support academic research across disciplines. These computing resources include access to multi-node clusters with thousands of CPU cores, hundreds of GPUs, and other specialized hardware.
These systems are available to ASU faculty, staff, students, and approved collaborators. Services are designed to enable large-scale data analysis, machine learning, simulations, modeling, and visualization.
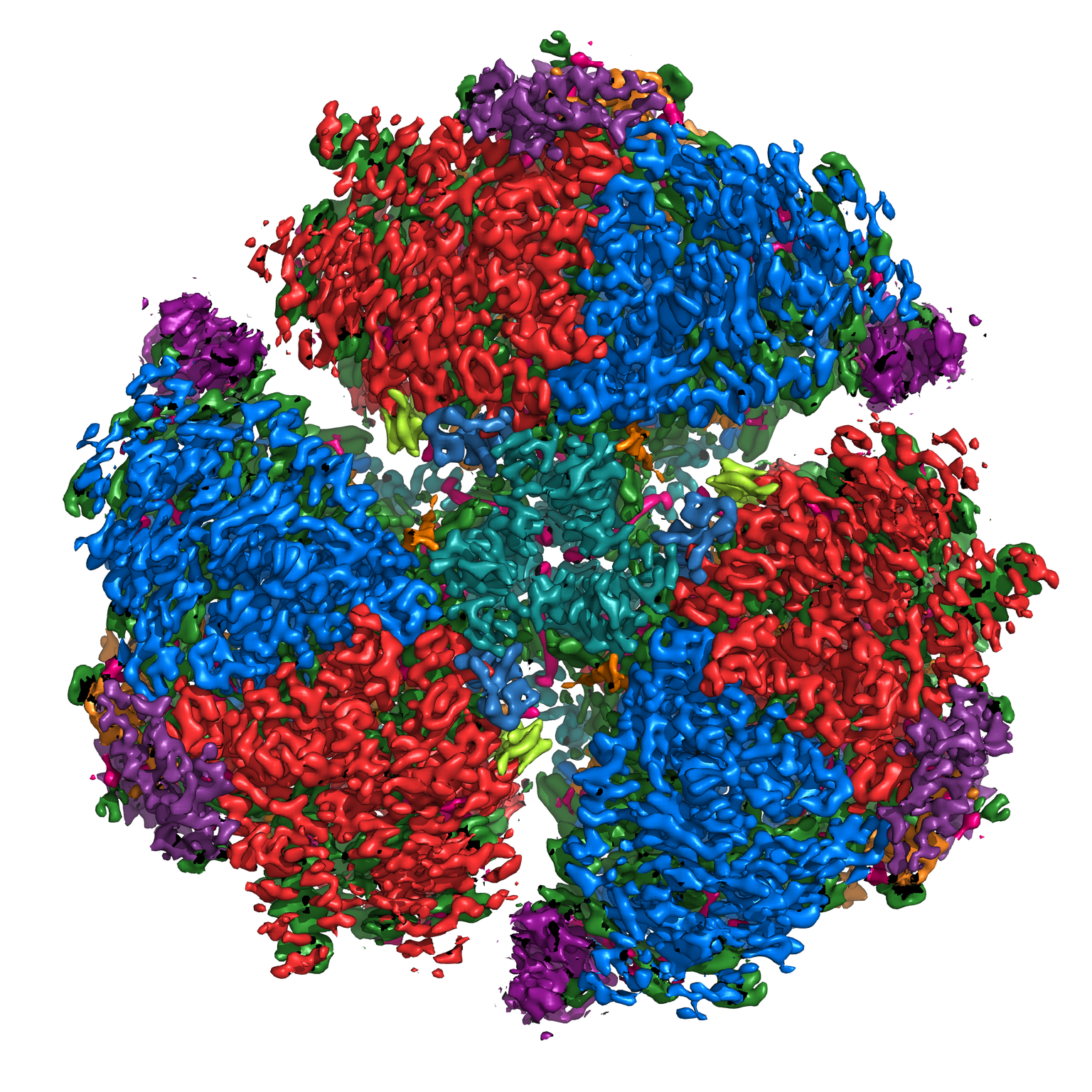
Visualization of a protein found in chlorophyll, produced by Yuval Mazor (School of Molecular Sciences) on the Agave supercomputer.
Available Supercomputing Systems
Sol Supercomputer
- Primary research computing cluster at ASU
- Personally funded by President Crow
- Multi-user, multi-project environment
- Free access for ASU researchers
Phoenix Supercomputer
- Legacy system (formerly Agave)
- Supports legacy workloads and specialized software environments
Aloe Supercomputer
- HIPAA-compliant computing environment
- Designed for research involving protected or controlled data
- Access through KE Secure Cloud (paid)
Cost Structure
| System | Access Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sol | Free | Fairshare scheduling based on historical usage |
| Phoenix | Free | Availability may vary |
| Aloe | Paid | Requires KE Secure Cloud access and data review |
Fairshare is a scheduling policy that dynamically prioritizes jobs based on recent usage to ensure equitable access.
CPU-Hour Usage
CPU usage is measured in CPU-hours, calculated as:
CPU-hours = Number of CPU cores × Runtime (in hours)
Example:
A job that runs for 2 hours on 16 cores = 32 CPU-hours.
This metric is used to track resource consumption and enforce scheduling policies.
Usage Guidelines
There is no hard cap on compute time or job submissions. However:
- High usage may result in longer wait times due to Fairshare.
- Jobs must follow policies regarding wall time, core limits, and node types.
To maintain efficient usage:
- Optimize code for parallel execution
- Use job arrays for batch processing
- Monitor resource usage frequently
When Should I Use a Supercomputer?
Use ASU’s supercomputing resources if:
- Your workload exceeds local workstation capabilities
- You require long runtimes or large-scale parallelization
- You work with large data sets or simulations
- You perform machine learning, deep learning, or GPU-based computing
- You require access to specialized hardware (e.g., high-memory nodes or GPUs)
Additional Help
If you require further assistance, contact the Research Computing Team:
- Ticket-based support via RTO Request Help Portal.
- Slack support via the #rc-support channel in the ASU Research Computing workspace.
- Weekly office hours for one-on-one assistance.
We also offer Educational Opportunities and Workshops.