Using a Terminal Client
To interact with the supercomputer, users typically employ a terminal interface through a command-line or SSH client installed on their local workstation. Once connected, you can submit unattended jobs--tasks executed autonomously on the supercomputer without the need for continuous user interaction or maintaining an active session.
Examples
Connect via SSH
- Sol
- Phoenix
ssh -X asurite@sol.asu.edu
ssh -X asurite@phoenix.rc.asu.edu
Replace asurite with your own ASURITE username. Use -X to allow windowed (point-and-click) applications to open on your workstation desktop.
Recommended Terminal Clients
Here are some examples connecting with some of the more readily-available terminal clients.
PuTTY (Windows)
-
Straightforward and lightweight: PuTTY.
Use PuTTY to connect to supercomputer with your ASURITE login and password
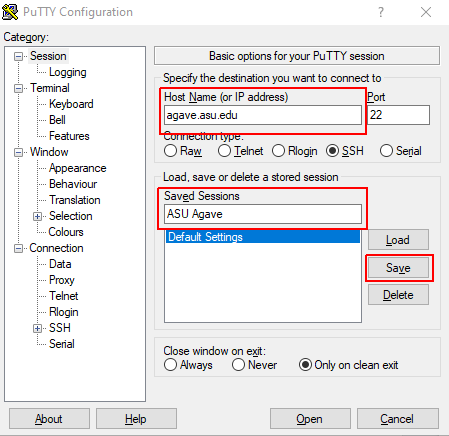
Enter in the hostname and use port 22.
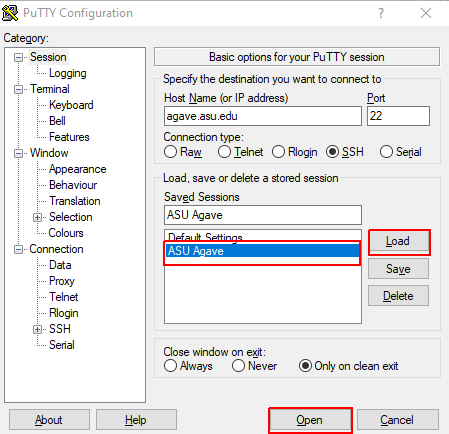
For convenience, give this session a memorable name in the "Saved Sessions" field. You can then save these settings for later, and easily load it again with the Load button.
Powershell (Windows 11)
- Powershell bundled with the operating system can be used with the above connection command.
WSL: Windows Subsystem for Linux (Windows)
- The ssh client that is included with the Windows Subsystem for Linux does not work with the Cisco VPN Client and is therefore unsupported.
Terminal (MacOS)
A simple tutorial on how to use the built-in SSH client on all MacOS versions can be found here: How To Use SSH on Mac OS X
Linux
Virtually every Linux distributions include an SSH client, and all are expected to work without issue.